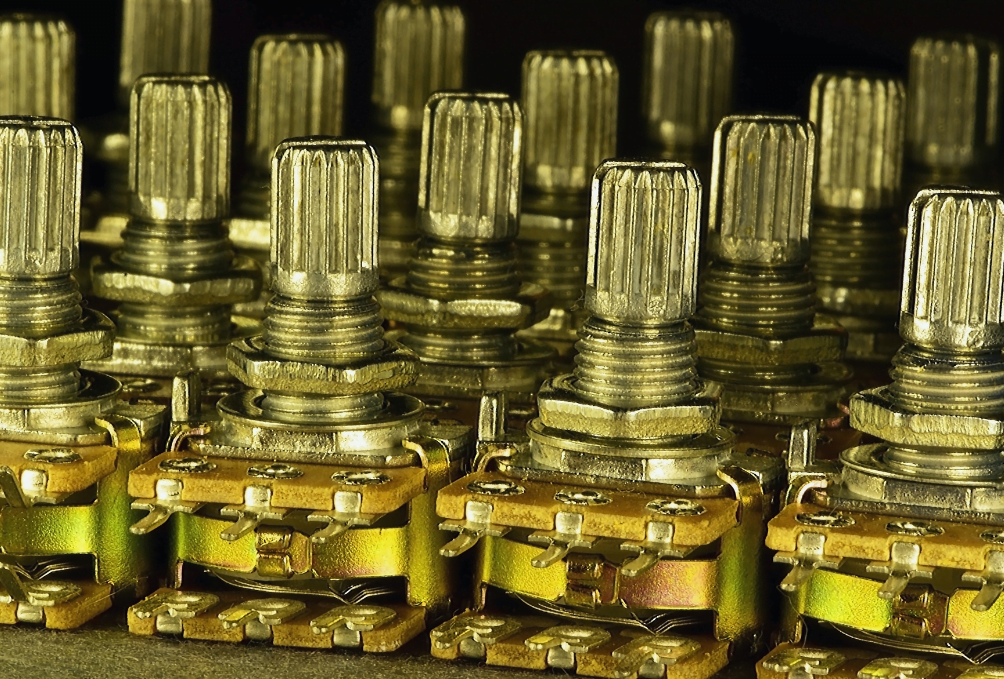
A potentiometer is an incredibly versatile electronic component widely used in many everyday devices. Its functions include adjusting various parameters such as volume, brightness, or electrical resistance in circuits. Although we often encounter it, many of us don’t consider how it works or what it is used for.
In this article, you will learn what a potentiometer is, how it works, and in which situations it can be applied. We will discuss various types of potentiometers, their construction, and practical examples of their applications.
Construction of a potentiometer
A potentiometer consists of several key elements. The most important are the resistor and the movable contact (called a wiper), which moves along the resistive track. When the user rotates the potentiometer knob, the wiper changes its position, affecting the resistance value between the contacts. This is how the potentiometer regulates the current flowing in the circuit.
The construction of a potentiometer may vary depending on the type. For instance, in slider potentiometers, a sliding wiper is used instead of a rotary knob. Regardless of the design, the principle of operation remains similar – changing the wiper’s position alters the resistance.
How does a potentiometer work?
The operation of a potentiometer is based on changing the resistance in a circuit. When the user rotates the knob, the wiper moves along the resistive track, affecting the resistance values between the contacts. Depending on the wiper’s position, the potentiometer can function as a voltage divider or a variable resistor.
When a potentiometer functions as a voltage divider, it alters the output voltage proportion relative to the input voltage. Conversely, when it acts as a variable resistor, it controls the amount of current flowing through the circuit. In both cases, the user gains control over circuit parameters.
Types of potentiometers
Potentiometers are categorized into several types based on their construction and application. The most common types are rotary, slider, and multi-turn potentiometers. Rotary potentiometers are the most popular type, used, for example, to adjust volume in audio equipment. Slider potentiometers are used where precise adjustment is required, such as in audio mixers.
Multi-turn potentiometers offer even greater precision since the wiper must make several full rotations to reach the extreme positions. They are used in applications requiring highly accurate parameter adjustments.
Applications of potentiometers in electronics
Potentiometers are ubiquitous in the world of electronics. In audio equipment, they control volume; in televisions and monitors, they adjust brightness; and in meters, they provide calibration. In each case, potentiometers enable smooth parameter adjustments to suit the user’s needs.
Another example of a potentiometer application is controlling the rotational speed of electric motors. In this case, the potentiometer regulates the voltage supplied to the motor, allowing control over its speed. This capability is crucial in many devices, from drills to industrial robots.
The potentiometer as a voltage divider
A potentiometer often serves as a voltage divider, dividing the input voltage into two different output voltages. The user can adjust the output voltage value by changing the wiper’s position. This allows for precise voltage regulation in electronic circuits.
An example of using a potentiometer as a voltage divider is adjusting the brightness of LEDs. By changing the wiper’s position, the voltage supplied to the diode can be increased or decreased, affecting its brightness. This simple solution is used in various devices, from flashlights to advanced lighting systems.
The potentiometer as a sensor
A potentiometer can function as a position or rotation angle sensor. In such applications, the potentiometer converts mechanical motion into an electrical signal, which can then be read and processed. An example is the use of potentiometers in joysticks, where the movement of the control stick translates into resistance changes.
In automation systems, potentiometers are used as position sensors, for instance, to monitor the position of valves. The changing signal from the potentiometer allows precise determination of the moving element’s position and adjustment of the control system accordingly.
Durability and quality of potentiometers
Choosing the right potentiometer depends on the application’s requirements. Key criteria include durability, quality of construction, and adjustment precision. Potentiometers made from high-quality materials offer longer service life and more stable operation. Particular attention should be paid to potentiometers used in demanding or high-intensity environments.
High-quality potentiometers can operate reliably for many years, making them indispensable in applications requiring dependability. It is essential to review the manufacturer’s specifications to select a potentiometer suitable for the specific application.
Choosing the right potentiometer
Selecting a potentiometer depends on several key parameters, such as the resistance adjustment range, housing type, and mounting method. Before purchasing, the application requirements should be clearly defined to ensure the potentiometer meets all necessary functions. It is also important to consider resistance tolerance, the acceptable deviation range from the nominal resistance value.
For instance, in applications requiring high precision, it is better to choose a potentiometer with low tolerance. Conversely, in less critical applications where precision is not paramount, potentiometers with higher tolerance, which are often more affordable, can be used.
Digital potentiometers
Modern electronics increasingly utilize digital potentiometers, which offer greater precision and the ability for remote control. Unlike traditional potentiometers, digital potentiometers regulate resistance using digital signals. This solution eliminates mechanical wear and enables integration with automated systems.
Digital potentiometers are used in advanced systems, such as power amplifiers or audio systems. They allow precise parameter control without the need for physical interaction with the device, significantly enhancing their versatility and application scope.
FAQ – Questions & Answers – What is a potentiometer?
Yes, a potentiometer can function as a position or rotation angle sensor. In such applications, mechanical motion is converted into an electrical signal.
The most common types of potentiometers are rotary, slider, and multi-turn. Each type has specific applications depending on the needs of the system.
An analog potentiometer adjusts resistance through physical movement of the wiper, whereas a digital potentiometer uses digital signals to change resistance. Digital potentiometers are more precise and resistant to wear.
Potentiometers are commonly used in audio equipment, screen brightness adjustments, meter calibration, and as position sensors in automation systems.