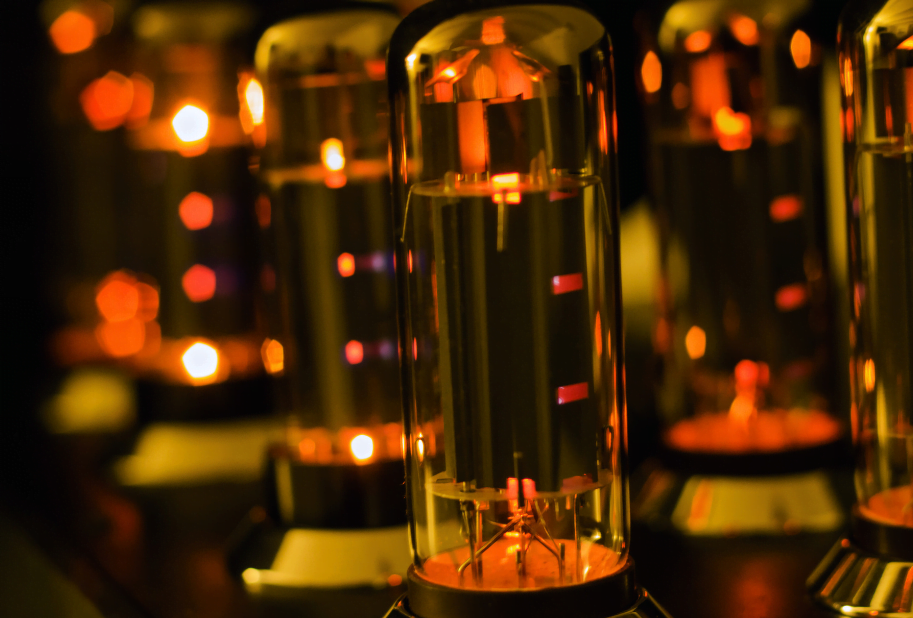
Electron tubes, although considered relics of the past today, still play a significant role in various technology fields. These unassuming glass bulbs filled with a vacuum were crucial for the development of electronics in the 20th century before transistors took over. However, despite technological progress, electron tubes still find their application, and their unique properties continue to fascinate.
In this article, you will learn what electron tubes are, how they work, and what their applications are in today’s world. We will also analyze their advantages and disadvantages compared to modern solutions like transistors and explore their future.
History of Electron Tubes
Electron tubes revolutionized electronics in the early 20th century. John Ambrose Fleming invented the first vacuum diode in 1904, marking the beginning of the electronics era. Shortly after, Lee De Forest created the triode, enabling signal amplification and the development of radio and telephony. Electron tubes became the foundation of communication, computer, and military technology for many decades.
However, with the emergence of transistors in the 1950s, tubes began to lose popularity. Transistors were smaller, more reliable, and consumed less energy. Nevertheless, electron tubes did not disappear entirely from the market. Their unique properties, such as the ability to operate in extreme conditions, are still valued in certain applications.
Principle of Operation of Electron Tubes
Understanding how electron tubes work requires some knowledge of electrons and their movement. In essence, an electron tube is a device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. The key element of any tube is the cathode, which emits electrons when heated. These electrons move to the anode, creating an electric current. Depending on the tube’s design, this flow can be controlled, allowing for signal amplification or radio wave generation.
Triodes, pentodes, and other more advanced types of electron tubes allow for more sophisticated signal control. Although the principle of operation remains simple, engineers have perfected these devices over the years to achieve better operating parameters.
Use of Electron Tubes in Audiophiles
They have found a special place in the hearts of audiophiles. Despite being expensive and harder to operate, tube amplifiers offer unique sound that many enthusiasts consider superior to what transistor amplifiers offer. Warm, rich sounds and natural compression are characteristics that distinguish tube amplifiers.
Audiophiles claim that electron tubes introduce a “soul” into music that modern solutions lack. Although technology has advanced, in the world of high-end audio, they still have their place, and their popularity remains strong.
Electron Tubes in Radiocommunications
They played a crucial role in the development of radiocommunications. Their ability to amplify signals and generate radio waves made them a fundamental element in radio and television transmitters. Even today, in some applications, electron tubes remain irreplaceable.
In high-power transmitters, especially in military and space applications, electron tubes still dominate. Their resistance to radiation and ability to operate in extreme temperatures make them indispensable in certain applications where transistors simply cannot replace them.
Electron Tubes in Microwave Technology
Microwave technology is another area where electron tubes play a crucial role. Klystrons and magnetrons, which are types of microwave tubes, are used in radars, satellite telecommunications, and microwave ovens. Their ability to generate high frequencies with high power is invaluable.
Although modern semiconductor devices replace tubes in many applications, some of them remain irreplaceable. High reliability and the ability to operate at high power give them an edge.
Summary
Electron tubes are electronic devices that use electron emission to generate current or amplify electrical signals. They have a wide range of applications in electronics, telecommunications, military technology, and medicine. Some examples of electron tubes include vacuum tubes, triodes, pentodes, and cathode ray tubes. These tubes are extremely durable and resistant to mechanical damage