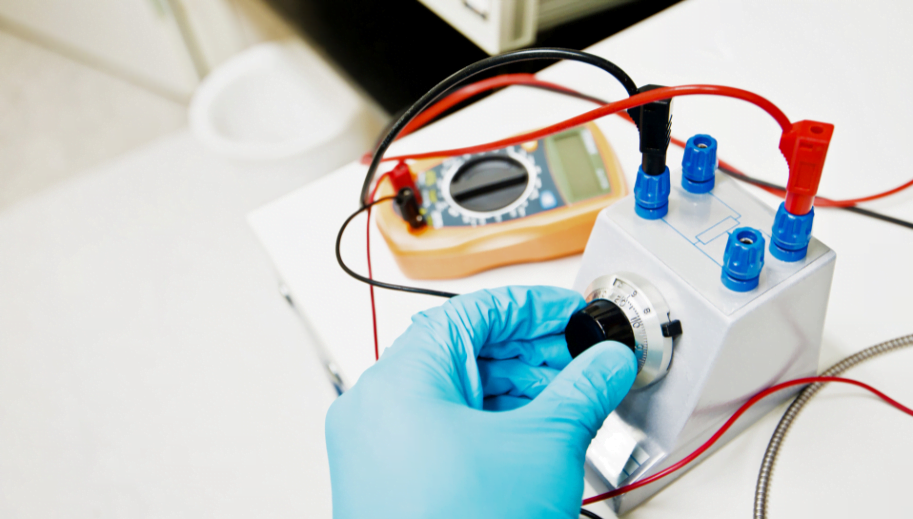
The voltage divider is a fundamental component in electronics and robotics, used to control voltage in circuits. Understanding its function is essential for anyone diving into electronics.
What is a Voltage Divider?
A voltage divider is an electronic circuit that allows a lower output voltage to be derived from a higher input voltage. It consists of two resistors connected in series. The output voltage depends on the resistor values, expressed by the formula U_OUT = U_IN * (R2 / (R1 + R2)).
Voltage dividers are widely used, from educational circuits to advanced measurement systems. Potentiometers, a type of resistive voltage divider, provide smooth voltage regulation, crucial for applications like volume control in audio devices. They also enable accurate voltage measurement in voltmeters by splitting the input voltage for better readings.
Construction of a Voltage Divider
A voltage divider comprises two resistors, R1 and R2, connected in series. The input voltage is applied across the entire circuit, while the output voltage is taken from the point between the resistors. This simple setup precisely divides the voltage within a circuit.
Ohm’s Law provides the formula U_OUT = U_IN * (R2 / (R1 + R2)) to calculate the output voltage. This enables tailoring resistor values for specific applications, making voltage control an essential feature in many electronic systems, from educational projects to advanced measurement setups.
Types of Voltage Dividers
The most common type is the resistive voltage divider, consisting of two resistors connected in series to split the input voltage. Capacitive dividers use capacitors and are often employed in high-voltage applications like generators or filters. Inductive dividers, made with coils, are used in AC circuits for voltage division and separation.
Each type has specific advantages depending on the application. Resistive dividers suit low-voltage systems, capacitive dividers excel in precision tasks, and inductive dividers handle specialized engineering challenges, offering versatility across industries.
Applications of Voltage Dividers
Voltage dividers are integral to electronics. Potentiometers, used for smooth voltage adjustments like audio volume control, exemplify their application. They enable user-friendly control by adapting voltage levels based on user input.
In microcontroller circuits, voltage dividers facilitate measurements by converting changes in physical properties (like temperature) into readable electrical signals. This functionality is critical in automation and monitoring systems requiring precise data acquisition.
Summary
The voltage divider is an essential circuit element for voltage regulation and measurement. Its simple yet versatile design allows for broad applications across electronics, from educational purposes to advanced systems. Understanding its function and types is crucial for effective use in practical applications.