The lever rule is one of the foundational principles in classical physics, explaining how force equilibrium operates in lever systems. This principle has allowed humans to amplify physical capabilities and effectively utilize tools for centuries.
What is the Lever Rule?
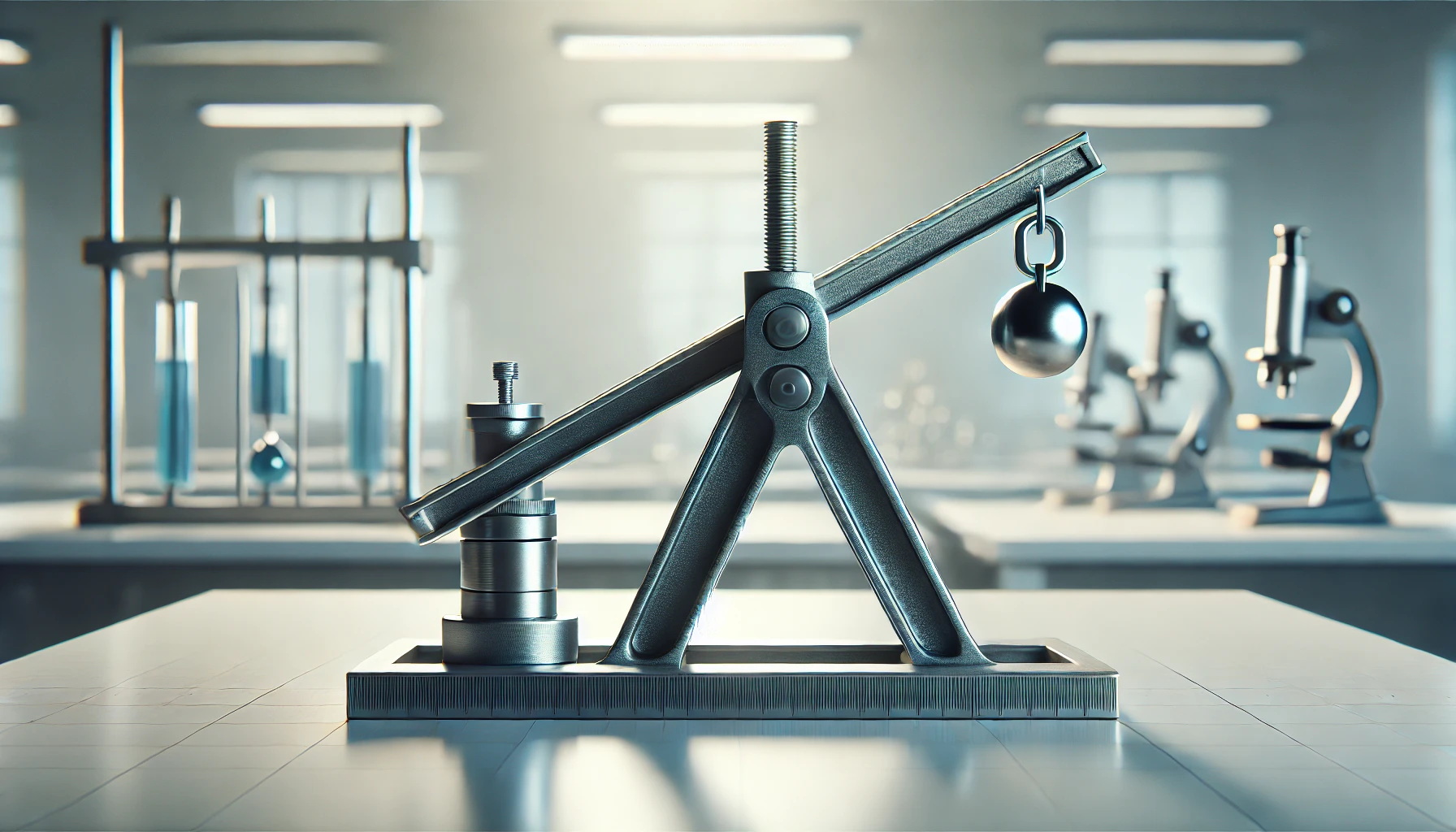
The lever rule is a physical principle that describes the relationship between force, the lever arm, and the effect of the applied force. A lever system consists of a beam and a fulcrum, which acts as the pivot point. By using a lever, it is possible to apply less force to lift heavier objects or perform work at greater heights.
How Does a Lever Work?
The fundamental equation of the lever rule is:
F_1 \cdot r_1 = F_2 \cdot r_2,
Where:
- F_1 and F_2 are the forces acting on the lever,
- r_1 and r_2 are the distances from the fulcrum to the points of force application.
The rule states that the moments (force multiplied by distance) must be equal on both sides of the fulcrum for the system to be balanced. This enables heavy objects to be lifted with relatively little effort.
Practical Example
Imagine you need to lift a 100 kg rock. By positioning the fulcrum closer to the rock, a force of only 10 kg is required if your lever arm is ten times longer than the arm on the rock’s side. This demonstrates the balance of forces using the lever rule.
Types of Levers
In physics, three basic types of levers are distinguished based on the arrangement of forces, arms, and the fulcrum.
First-Class Lever:
- The fulcrum is located between the applied force and the load.
- Example: A seesaw on a playground.
Second-Class Lever:
- The load is positioned between the applied force and the fulcrum.
- Example: A wheelbarrow used for carrying materials.
Third-Class Lever:
- The applied force is between the load and the fulcrum.
- Example: Tweezers or surgical forceps.
Summary
The lever rule is a cornerstone of classical mechanics and a practical tool in everyday life. From lifting heavy objects to designing precise machines, its applications are vast. Understanding the lever rule helps optimize force and energy usage in various fields, making it an invaluable principle in both science and engineering.