Ultrasonography is a diagnostic tool that has revolutionized medicine. This non-invasive method allows imaging of the inside of our body using sound waves. Whether a patient requires a heart examination, pregnancy monitoring, or internal organ analysis, ultrasonography plays a crucial role in diagnosis and treatment.
In this article, you will learn exactly what ultrasonography is, its types, and when doctors use this technique. We will also present the key benefits of its application and how to prepare for the examination to ensure its effectiveness.
What is Ultrasonography?
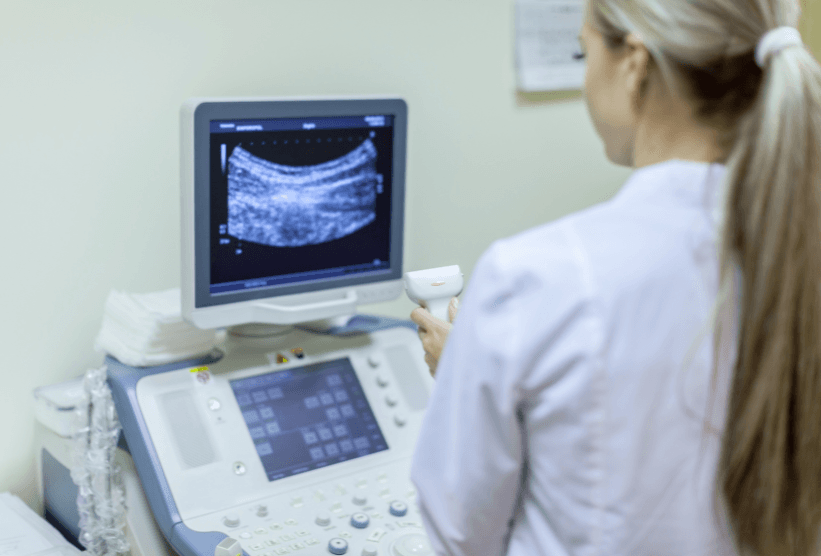
Ultrasonography is an imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body’s interior. Unlike X-rays, ultrasonography does not use ionizing radiation, making it completely safe for patients of all ages, including pregnant women. The examination is performed by a specialist using a transducer (probe) that emits sound waves and receives their echoes, creating an image on the monitor.
Ultrasonography provides detailed information about soft tissues, internal organs, and the circulatory system. This examination does not require invasive procedures, meaning the patient does not have to undergo surgery or endure pain. Ultrasonography is fast, and its results can be immediately analyzed by the doctor, enabling a quick diagnosis.
Ultrasonography plays a key role in healthcare worldwide. It helps diagnose organ diseases, detect tumors, assess blood flow, and monitor fetal health. It is also used to assist doctors during procedures such as biopsies or injections.
Types of Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography offers several different types of examinations, each with its specific application. One of the most commonly used is abdominal ultrasound, which allows for the evaluation of organs such as the liver, pancreas, or spleen. This examination helps diagnose inflammations, tumors, and gallstones.
Another important type of ultrasonography is echocardiography, a heart examination. This test allows doctors to assess heart function, its valves, and blood flow through blood vessels. It is used for diagnosing heart defects and monitoring treatment effects.
We cannot forget about Doppler ultrasonography, which evaluates blood flow in arteries and veins. This allows doctors to detect clots, vascular narrowing, and other problems related to the circulatory system. Doppler studies are particularly important for patients at risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Applications in Medicine
Ultrasonography is used in many fields of medicine. In gynecological diagnostics, ultrasonography allows for the assessment of female reproductive organs such as the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Through ultrasound examinations, doctors can detect cancerous changes, cysts, and other abnormalities.
In internal medicine, ultrasonography helps evaluate organs such as the liver, kidneys, stomach, and gallbladder. It enables the rapid detection of inflammations, tumors, and even internal bleeding, which can save a patient’s life.
In sports diagnostics, ultrasonography is used to evaluate the condition of muscles, tendons, and ligaments. It helps detect injuries such as tears or inflammation and assess the effectiveness of the rehabilitation process.
Preparing for an Ultrasound Examination
Preparation for ultrasonography depends on the type of examination to be performed. For abdominal ultrasound, patients often need to refrain from eating for several hours before the test. A clear image depends on an empty stomach, allowing a more detailed view of the organs.
For pelvic or pregnancy ultrasounds, the patient may need to drink an appropriate amount of water to fill the bladder. A full bladder enhances the image quality of the uterus and other structures.
It is always advisable to dress comfortably and avoid jewelry to facilitate the examination. In case of any doubts, it is best to consult with a doctor or medical staff.
Benefits of Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography offers many advantages, making it a preferred diagnostic method in many cases. Firstly, it is a safe method because it does not use radiation, and its non-invasive nature eliminates the need for surgeries.
Additionally, ultrasonography is fast, meaning patients do not have to wait days for test results. Doctors can immediately analyze the images and decide on further treatment. Ultrasonography is also less expensive than other diagnostic methods like computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), making it accessible to more patients.
Another significant advantage of ultrasonography is its versatility. Doctors can use it to image almost any internal organ, monitor pregnancies, and perform diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Ultrasonography vs. Other Imaging Techniques
Compared to other imaging techniques, ultrasonography stands out primarily for its lack of radiation-related risks. Computed tomography (CT) and X-rays use ionizing radiation, which can affect patients’ health, especially with repeated tests.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), on the other hand, requires extended time in a closed machine, which can be difficult for individuals with claustrophobia. Ultrasonography is quick, comfortable, and does not require staying in tight spaces, increasing patient comfort.
However, it is worth noting that ultrasonography is not always the best choice. It is not suitable for imaging dense structures like bones or organs containing air, such as the lungs. Therefore, doctors often combine various imaging techniques to get a complete picture of the patient’s health.
How is an Ultrasound Examination Conducted?
During an ultrasound examination, the doctor or technician uses a transducer to send sound waves into the body. The transducer receives the reflected waves and converts them into an image visible on the monitor. The patient usually lies on a bed, and a special gel is applied to the skin to improve sound wave conduction.
The examination typically lasts 20 to 60 minutes and is entirely painless. For certain types of ultrasound, such as transvaginal exams, there may be slight discomfort, but it is usually short-lived. After the examination, the doctor removes any excess gel, and the patient can immediately resume normal activities.
Doctors analyze the results immediately after the examination or send the images to a radiologist who prepares a detailed report. Ultrasonography provides valuable information, enabling quick diagnosis and treatment decisions.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography is safe, fast, and non-invasive. It does not use radiation, making it safe even for pregnant women. The test is also relatively inexpensive and widely available.
Yes, it can detect tumors and help distinguish them from cysts. The test is often used for the initial assessment of cancerous changes.
Yes, preparation depends on the type of examination. For abdominal ultrasound, you may need to refrain from eating. For pelvic tests, you may need to drink an adequate amount of water.
No, ultrasonography is painless. In some cases, such as transvaginal ultrasound, there may be slight discomfort, but it is short-lived.